Ultimate Guide on Cambodia Property Tax
Cambodia Property Tax is a very important aspect that foreign investors need to understand when planning to purchase real estate property in Cambodia. There had been a lot of changes in the past decade wherein existing laws that were not previously followed are now more rigorously being implemented and additional laws are being introduced or in future consideration.
This article will explain in detail, from reports of the General Department of Taxation (GDT), the taxes that directly affect investors that own or plan to purchase real estate properties and businesses in Cambodia.
Scroll down to the details in the below-mentioned sections to know all about what is property tax, how to calculate property tax in Cambodia, property tax formula, property tax registration, property tax receipt, and other details that a property owner in Cambodia must be informed of.
Cambodia Property Tax
This tax aims to encourage the use of land and benefit the sub-national administrative budget. Property tax, officially known as TOIP or Tax on Immovable Properties, is imposed to properties located in the municipality and provinces that are more than 100 Million Riel ($25,000) in value.
- The term “Property” refers to lands, houses, buildings and other constructions that are built on the land.
- Property tax is collected annually at the rate of 0.1% on the property. According to the property tax formula, the tax base is the value of the land and the constructions that are built on that minus $25,000.
- The value of lands, houses, buildings, and other constructions that are built on the land is determined based on the market price by the property evaluation committee established by the Prakas of the Minister of Economy and Finance.
- Tax base varies depending on Building type, elevation, specific area of the property (main road vs side road) and age of the building. Generally, buildings that are more than 10 years old and condominium buildings are taxed higher.
How to compute Property Tax?
When computing for Property Tax, it can be derived by getting the 80% of the tax base (price based on assessment by the Prakas of the Minister of Economy and Finance) then subtracting $25,000 (tax exemption) and getting 1% of the total.

APPENDIX
Prices in the table are actual determined land and building price per square meter properties located within Khan Daun Penh, Khan 7 Makara, Khan Chamkarmon and Khan Tuol Kork.
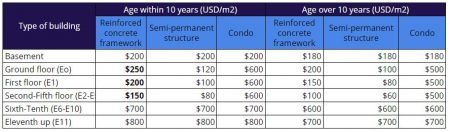
In the sample computation below, we look at the assumption that this homeowner has a 4 storey apartment in Khan Daun Penh. We assumed that the land price is $1,500 per sq.m. and the building is reinforced concrete built in the last 10 years. Using the above table, tax base is calculated per floor of the building and then computed using the property tax calculation previously used. We will then arrive at this estimate:
Property Tax = (($292,500)*80%)-$25,000)*0.1% = $209
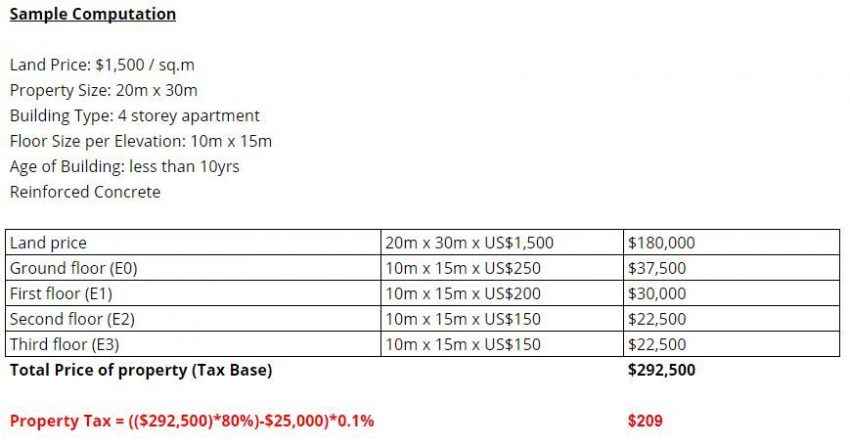
Please note that this is only a sample computation and may vary depending on specific location and how the land ownership is subdivided between unit owners in a condominium building.
Tax on Unused Land
The Unused Land Tax is imposed on non-constructed land and the abandoned constructed land which are located in the cities and the areas determined by the Unused Land Appraisal Committee (ULAC).
- The Unused Land Tax is the responsibility of the property owner and is required to be paid by the 30th of September each year
- The Tax Base is the actual value of the land evaluated in square meter and imposed by the ULAC every June 30th every year
- The Unused Land Tax is a 2% fee on the tax base
- This type of tax on land discourages owners from not using or appropriating valuable property specially on prime city locations.
- Tax on unused land applies only to land with a value less than 100 Million Riel, as determined by the Land Appraisal and Valuation Committee.
Sample Computation
Land around market and main road in Old Market (Phsar Chas) – Price $1,000/sq.m
Land Size – 200 sq.m
Base Tax = ($1,000*200)*0.2%(Unused Land Tax) = $400
Tax on Property Rental
Property rental Tax is set by the rental received on the following types of properties:
- Residential and Commercial Buildings or properties
- Industrial and commercial installed equipment
- Floating homes or ships used as homestay or place of business
- Land without buildings used for stone, mine and coal extraction, lakes and salt pan field
- This tax is collected from proprietors or lease holders.
The tax rate is equivalent to 10% of the gross rental. This gross rental is included in the lease agreement.
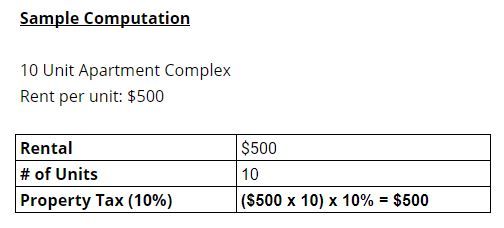
Some apartment complexes may have different rental prices per unit. Tax base is computed from the Gross of all rentals. There are properties wherein an additional 10% is added on the lease agreement to offset the property rental tax being paid by the owner.
Registration Tax
Registration Tax, also known as Transfer tax, is a 4% tax imposed on transfer of ownership of real estate property or transfer of occupancy rights of land without building in the form of sale, exchange, receiving gift or putting capital in company. According to tax law, the buyer is responsible for the payment of the 4% stamp tax, however in practice, it is the seller that most commonly pays.
- Prokas No. 273 of MEF: Article 5 Section B. (Selling excluded) – This Prokas refers to Tax Exemption (Signed by Prime Minister Hun Sen on January 10, 2016) on properties that had been transferred to direct kin or relatives via inheritance. This directive states that “transfers between spouses, parents and children, or grandparents and grandchildren, will no longer require this tax”
- This tax is also applicable for government seized and/or foreclosed properties acquired through silent bidding. When negotiated, it can be applied against the actual bidding price.
Sample Computation
Registration Tax = (Tax Base*0.4%)
Base Tax (derived from previous table) = $292,500
Registration Tax = ($292,500*4%) = $1,170
Patent Tax
This type of tax is specific to business owners and classified into 3 categories.
- Small taxpayers are Sole Proprietorship or Partnerships – Business owners that have annual taxable income from 250 Million Riel ($62,500) to 700 Million Riel ($175,000)
- Medium taxpayers are Enterprises that are incorporated as legal entities, Sub-national government institutions, associations, and non-governmental organization that have annual turnover from $175,000 to $500,000
- Large taxpayers are Enterprises registered as a Qualified Investment Project (“QIP”) and approved by the Council for the Development of Cambodia, Government Institutions, foreign diplomatic and consular missions, international organizations and agencies that have annual turnover over $500,000
THINGS TO REMEMBER
- Taxpayers with multiple business activities need to pay a separate patent tax for each activity.
- If the additional business is in line with the main business activity, it will be considered as one for patent tax purposes.
- If the business has a branch office, warehouse, factory or workshop in a different location or city, they are required to pay an additional Patent Tax fee of 3 Million Riel ($750) to the tax authority where the additional branch is located.
- A business with a branch office, warehouse, factory and workshop in the same location (city-province) is required to pay only one Patent tax fee.
- Taxpayers who started their business within the first 6 months of the year need to pay the patent tax in full while those that opened their business in the last 6 months of the year will need to pay only half the patent tax fee.
- If a business changes owners but stays the same, and the new owners are family or legal successors, then there is no need to pay additional patent tax.
Additional Taxes for Non-Residents
- INCOME TAX – is income earned by non-residents or foreign nationalities and generally taxed at a flat rate of 10%. This tax is imposed on “Cambodian-income” and calculated based on the income generated while working in Cambodia.
- RENTAL INCOME – is income from leasing real estate properties earned by foreigners and subject to withholding tax of 14%. Property rental tax is different and generally levied at 10% for property owners with Cambodian Citizenship. An additional 14% is required for foreigners.
- CAPITAL GAINS TAX – income earned by foreigners with business in Cambodia are subject to profits tax at a flat rate of 20%.
- CORPORATE TAX – Income and capital gains earned by foreign companies are taxed at the flat corporate tax rate of 20%. Income-generating expenses are deducted when calculating taxable income.
Penalties on Tardiness and Tax Evasion
Except for Vat returns which are set to the 20th of the month, the deadline for the filing and payment of tax returns is the 15th of the month for Monthly Tax Returns and the 31st of March for the Annual Tax on Profit and Patent Tax. If an audit made by the Local Khan or the General Department of Taxation results in a reassessment of tax pricing, the tax payment is declared late because it’s not paid correctly on the due date.
- Late payment incurs a penalty of 10% to 40% of the tax amount plus 2% interest per month on the underpaid taxes and late filing of the return, which is 2 Million Riel (approximately US$500).
- Additional penalties applied for violations against the Law on Taxation and other regulations:
- Negligence (Sec 9 Article 125) – If the tax deficit is because of negligence and variance is less than 10%, the penalty is 10% of the unpaid tax amount.
- Serious Negligence (Sec 9 Article 126) – Deficit is due to serious negligence for tax variance of more than 10%, the penalty is 25% of the unpaid tax amount
- Tax Evasion (Sec 9 Article 127) – Any serious violation of Article 126 committed on 2 separate occasions within 3 years or 2-3 separate instances within any given time is deemed in violation of this article and the penalty is 40% of the unpaid tax amount
General Department of Tax Debt Collection
In a report published by the Council for the Development of Cambodia (CDC), it is explained that tax liabilities should be paid within 30 days of the notification letter of tax debt collection. If the taxpayer fails to meet the deadline, a reminder letter will be sent out within 15 days before schedule of debt collection. If the taxpayer still did not pay within this time, enforced tax debt collection and unilateral tax assessment will apply.
Per Prakas No. 74 (signed in 2008),
“As provided in article 109 of the letter taxation, the delivery of a reminder letter of notification for tax collection establishes a lien in favor of the tax administration over the properties of the taxpayer withholding agent who is the person liable to tax and who is named in that letter of notification.
- The properties of the person as stated in paragraph 1 of this section includes all properties whether movable or immovable, tangible or intangible, except for foodstuffs, clothing, cooking utensils, and objects of worship.
- The lien on movable or immovable property shall have validity and priority over all other rights existing before or after that lien on the liable person’s property.
- For the liable person who fails to pay the tax debt, penalties, and costs of tax collection within 15 days of the date of delivery of the reminder letter of notification for tax collection, the tax administration may confiscate the property of that person with the cooperation from the Police and the Territorial Authorities as may be necessary for the actual implementation of the confiscation measures.
- Can be subject to confiscation all properties of the liable person whether these properties are held by the liable person himself or by a third person. All properties found at the place of the liable person are presumed to belong to the liable person except for contrary evidence. Properties that are exempted from the imposition of a lien are also exempted from confiscation.”
Confiscation may include freezing of bank accounts, cancellation of import and export activities, cancellation of taxpayer’s business license, and Seizure and sale of property.
What to remember when paying your taxes?
Property Tax in Cambodia is not an exact science. It depends a lot on negotiation skills, the area where your property is located, and the evaluation of the Property Valuation officer assigned in your area. The prices listed here are sample computation to get an idea, or a ballpark figure, of what taxes to pay and approximately how much will be needed for properties that you want to acquire as an investment.
Unilateral Tax Assessment, Late filing of tax liabilities and Enforced Tax Collection carry huge penalties and are something that you need to avoid at all costs. Understanding the basic tax guidelines and the schedule of paying the appropriate taxes is the key to ensuring the security of your properties.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Are there any exemptions or deductions available for property tax in Cambodia?
Yes, exemptions and deductions are available for property tax in Cambodia, such as for state-owned land, agricultural land, and industrial land.
- How often is property tax assessed in Cambodia?
Property tax in Cambodia is assessed annually.
- Can property tax be paid online in Cambodia?
Yes, Cambodia’s property tax can be paid online through the General Department of Taxation’s website.
- How does property tax differ for residential and commercial properties in Cambodia?
Residential properties are taxed at a lower rate than commercial properties.
- How is property tax collected for properties owned by foreign companies in Cambodia?
Property tax for properties owned by foreign companies in Cambodia is collected through the withholding tax system.
- Can property tax be transferred to new owners upon property sale in Cambodia?
Property tax is not transferred to new owners upon property sale in Cambodia.
- Can property tax be paid in installments in Cambodia?
Property tax can be paid in installments in Cambodia, but only with the approval of the General Department of Taxation.
- How does property tax differ for vacant land and developed properties in Cambodia?
Vacant land is taxed at a higher rate than developed properties.
- Are there any property tax breaks for senior citizens or retirees in Cambodia?
Yes, Cambodia has property tax breaks for senior citizens or retirees.
IPS Cambodia
With an adept understanding of local real estate trends and markets, we deliver insightful, data-driven content that illuminates the Cambodian property scene. Our written pieces serve as a dependable resource, helping clients make informed decisions. With IPS, real estate expertise extends beyond transactions—it informs, engages, and educates.
2 thoughts on “ Ultimate Guide on Cambodia Property Tax ”
- Pingback: Types of Property Titles -
- Pingback: How to choose your first investment property in Cambodia – Golden Whale Properties
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Independent Property Services (IPS) has grown to be the premier real estate company in Cambodia, with offices located in Phnom Penh and Siem Reap providing premium real estate opportunities and catering to the local and expat market since 2009. Whether it is a new residence, commercial space, or land you seek, our property agents can present you with first-rate choices that fit your budget and lifestyle. IPS manages condominiums for rent, houses for rent, and apartments for rent in Phnom Penh, Siem Reap, and other properties are also available for rent and sale in throughout Cambodia.
Trusted Partner . Market Leader .
CONNECT WITH US 🙂
- Phnom Penh
- Siem Reap
- Property Valuations
- Property Management
- Document Processing Services
- Investor’s Guide
- FAQs
- Careers
- Contact Us
- Back to Home
#182, Street 63, BKK1, Phnom Penh, 120102 | #618, Corner Wat Bo Road and Street 24, Siem Reap, 171204





